Counseling and psychotherapy for individuals, couples and families.
Holistic Trauma Recovery and Sound Alchemy
Deeper Knowledge Awaits...
January 1, 2024
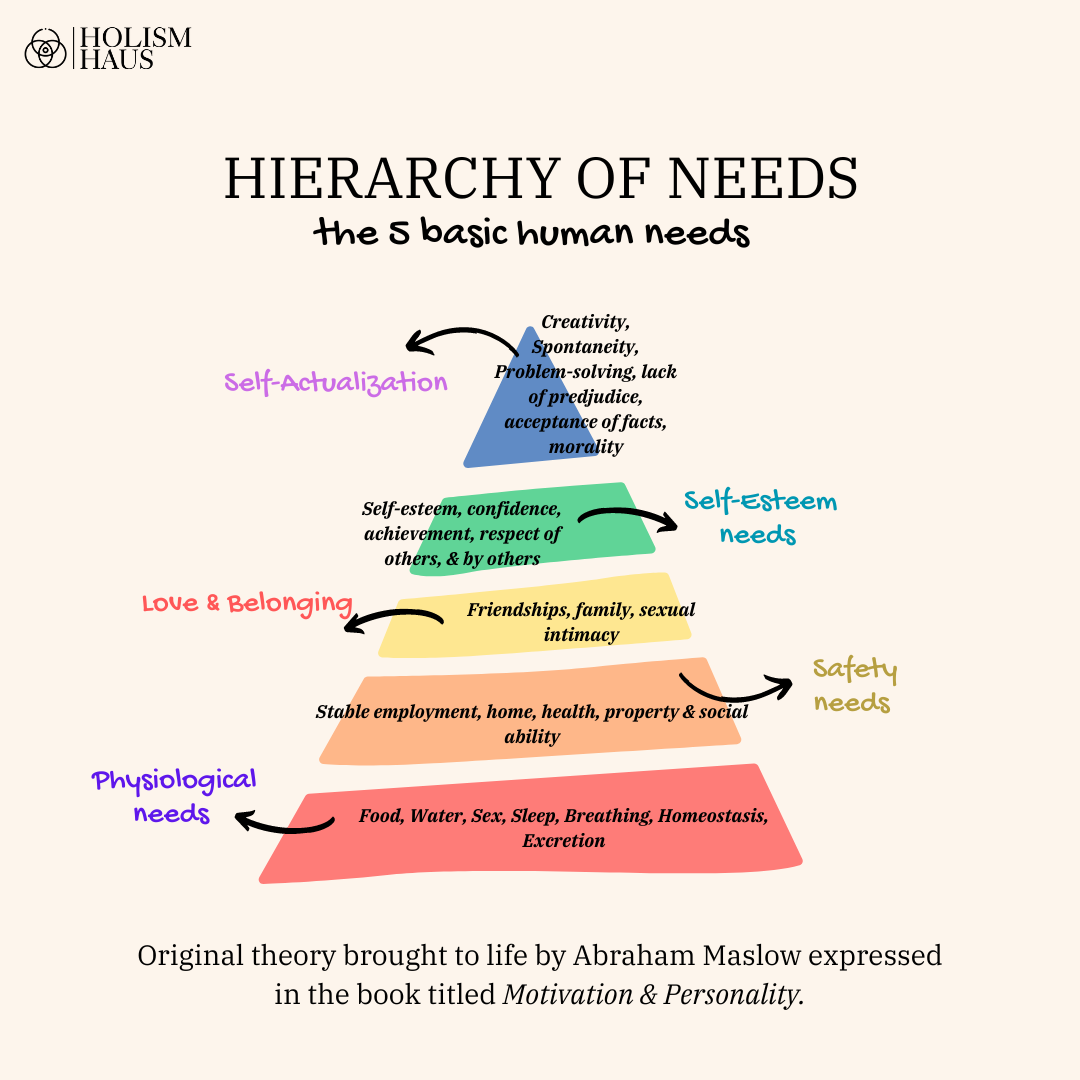
This concept was introduced by psychologist Abraham Maslow. The pyramid serves as a roadmap for understanding what drives human behavior and fulfillment. As it relates to trauma, and the mind, one's needs must be met physiologically first to regulate and move your body into a "safe" state, ironically the next phase of the hierarchy. The Pyramid of Human Needs: Physiological Needs: At the base of the pyramid lie our most fundamental needs—food, water, shelter, and sleep. These primal requirements must be met for survival and form the foundation upon which all other needs build. Safety Needs: Once our physiological needs are reasonably fulfilled, we seek safety and security. This encompasses personal security, financial stability, health, and protection from physical or emotional harm. Love and Belongingness: As we move up the pyramid, our focus shifts to social needs—affection, relationships, friendship, and a sense of belonging within communities or social groups. Esteem: Beyond social connections, we yearn for recognition, respect, and self-worth. Esteem needs involve both external factors like status, success, and prestige, as well as internal factors like self-confidence and accomplishment.

December 29, 2023
Trauma, in its various forms, casts a long shadow on our lives. Its effects ripple far beyond the emotional and mental realm, leaving an indelible mark on the body. For those raising teens and young adults, understanding how trauma affects us physically is crucial in fostering overall well-being.

December 21, 2023
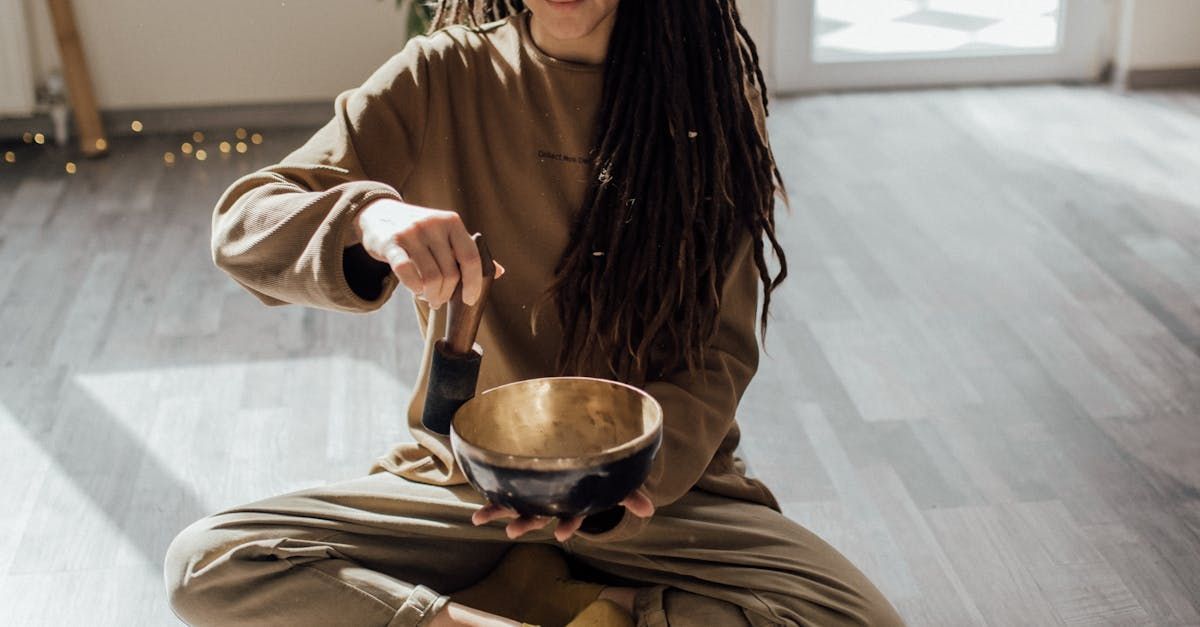
A sound bath is simply being present in the moment, experiencing sound waves and frequencies at a physical, and spiritual level. Simply put, it's just sitting or lying down and relaxing your mind. The results cannot be simply stated, though. I've had clients who have experienced serenity, visions, and bodily sensations during our sessions together. Our sound bowl instruments include: Quartz Singing Bowls Solfeggio Tuning Forks Ocean Drums

December 21, 2023
Of course, you do! Aromanifestation is a newly developed concept by Maranda Houston to combine aromas with the law of attraction principles and the spirit of herbs. Many aromatherapists use plant extracts to promote physical, mental and emotional well-being. These extracts are also called Essential oils. Essential Oils can be used in conjunction with herbal baths, as we provide, topical massages, or diffusers. Each herb is uniquely designed by the divine for a purpose, such as yours. The "spirit" of these herbs lives on to provide healing in multiple modalities like tinctures, teas, medicines, and salves.

December 15, 2023
Reconnecting with the body after trauma is a deeply personal journey. What works for one person might not work for another, so it's essential to explore and find what feels most comfortable and effective for you. Seeking professional help or guidance from a therapist or counselor specializing in trauma can also provide invaluable support in this process.
Let's Talk
The first step in coaching is talking. Let's find a time where we can meet and talk about what's on your mind, and how we can help!
Book a consultation